The alimentary canal has 3 parts:
- Foregut: oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, stomach
- Midgut: small intestine
- Hindgut: large intestine – caecum, colon, rectum

Humans are heterotrophic omnivores. -> gut processes many kinds of food
Enzymes:
- cleave the chemical bonds of macromolecules through addition of water (hydrolysis)
-> hydrolytic enzymes
- classified according to substrate
- protease, peptidase
- carbohydrase (maltase, lactase, sucrase)
- lipase
- nuclease
- produced in inactive form (= zymogene) – activated outside the cell (pH, other enzyme)
- proteins -> temperature, pH optimum
- digestive enzymes are produced by exocrine glands (= excrete onto outer surfaces)
- rER -> Golgi-> vesicles -> surface -> duct -> lumen
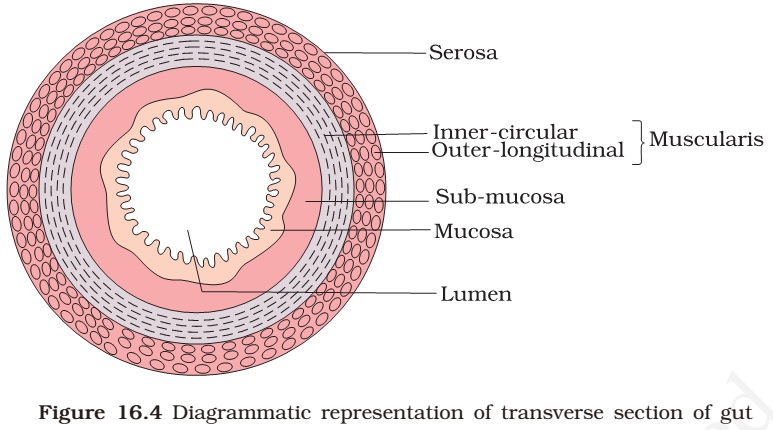
Histology of the gut
- Mucosa: epithelium
- Submucosa: connective tissue with blood and lymph vessels, nerves
- Circular smooth muscle: constricts the lumen
- Longitudinal smooth muscle: cells along the length of the gut, shorten the gut
- Serosa: connective tissue
Peritoneum: epithelium; thin membrane lining the abdominal cavity
- FOREGUT
1. Oral cavity
a) teeth
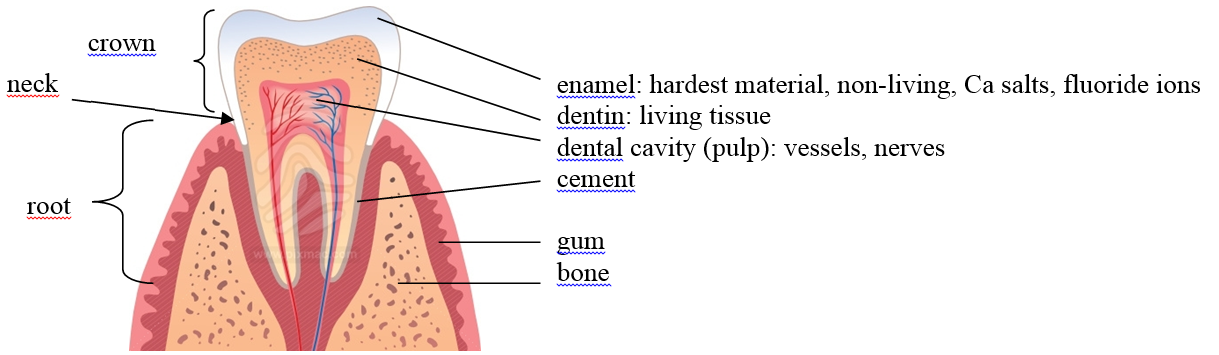
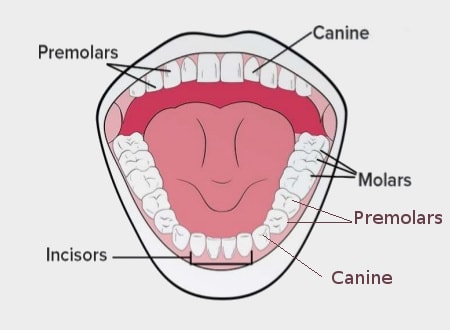
Types:
- incisors: sharp, at the front for biting
- canines: pointed, for tearing
- premolars: broad, flat surface for grinding (2 cusps)
- molars: last one is the wisdom tooth (4 or more cusps)
Number:
adults: 32 permanent teeth
children: 20 deciduous /primary/ teeth
appear from 6 month
fall out between 6-12ys
dental formula:
I.C.P.M.
I.C.P.M
adults: 2123 children: 2102
2123 2102 

Oral hygiene:
- clean teeth 3 times a day, after eating
- use dental floss
- clean your tongue

- gently massage gums with toothbrush
- mouth wash can be used
- Visit your dentist regularly
- remove plaque
- avoid snacks and too much sugar
- caries is caused by bacteria
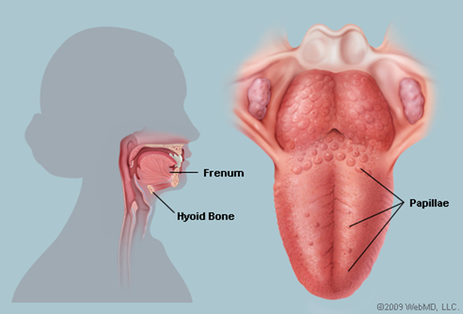
b) tongue
- taste organ –
taste buds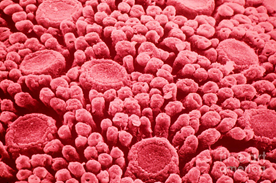
- helps chewing and forming a bolus (soft ball of food + saliva)
- moves the food into position for chewing
- helps swallowing
- takes part in speech
c) salivary glands
- produce saliva:
- 1-5 l /day
- moistens food
- water, dissolved ions
- mucus (lubricates food to move smoothly)
- salivary amylase:
- digestive enzyme,
- breakdown of starch and glycogen to maltose begins
- pH 7 – 7.2
- lysozyme enzyme -> damages bacterial cell wall -> slight antibacterial effect, but NO role in digestion
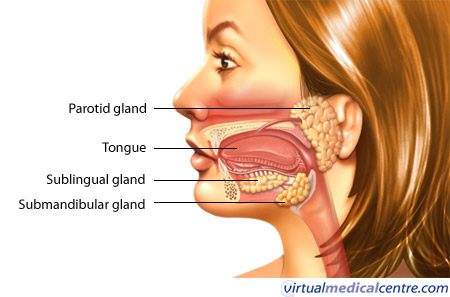
- 3 pairs of salivary glands: exocrine glands
- Parotid gland -> mainly amylase (25%)
- Sublingual gland: under tip of tongue -> mucus (5%)
- Submandibular gland: along lower jaw -> both (70%)
d) palate
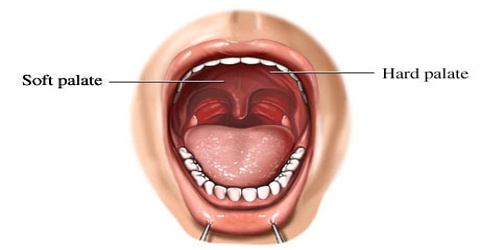
- hard palate:
- bony plate in the roof of the mouth
- helps speaking
- soft palate
- closes the path to the nasal cavity when swallowing
Swallowing
- bolus is pushed back by the tongue
- soft palate closes off the nasal cavity
- epiglottis seals off the trachea
- food gets into the pharynx
- pharynx contracts and pushes the bolus into the esophagus -> stomach
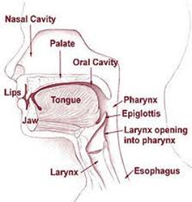
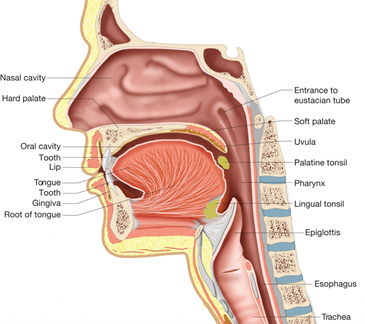
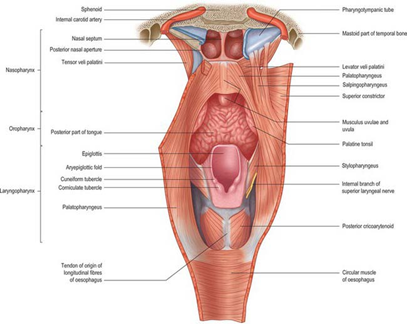
2. Pharynx
- Meeting point of nasal and oral cavity
- the food and air pathways cross each other in the pharynx
3. Oesophagus
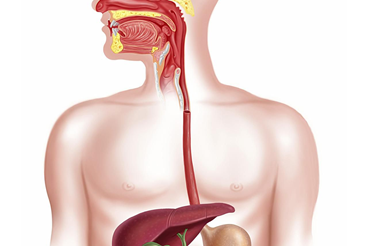
- connects the pharynx with the stomach
- 25-30 cm
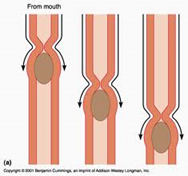
- Layers of muscle: longitudinal, circular
- Muscles move food along with wavelike movement -> peristalsis
- Upper 1/3 voluntary muscle
- Lower 2/3 smooth muscle
4. Stomach
a) Structure
- in the abdominal cavity
- J shaped, capacity to store 2-4 litres
- Cardiac sphincter:
- prevents food from re-entering the esophagus
- thick ring of muscle controlling circular opening
- pyloric sphincter: at the lower opening
- muscle layers: circular, longitudinal and diagonal layers
- glandular epithelium
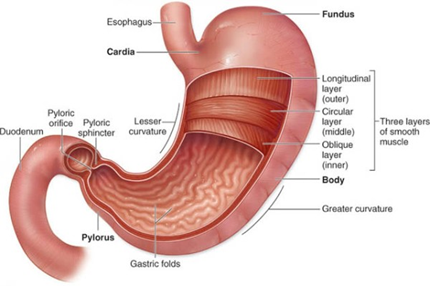
b) Function
- stores food and releases it into the intestine in small portions
- kills bacteria
- physical breakdown by peristalsis
- chemical breakdown: digestion of proteins
=> gastric juice
parietal cells -> HCl -> kills bacteria
-> pH2 -> for activation and functioning
-> amylase no longer works
chief cells -> pepsin
- proteins -> peptides
- pepsinogen +HCl -> active pepsin
mucous cells -> mucus: protects epithelial cells against enzymes and hydrochloric acid
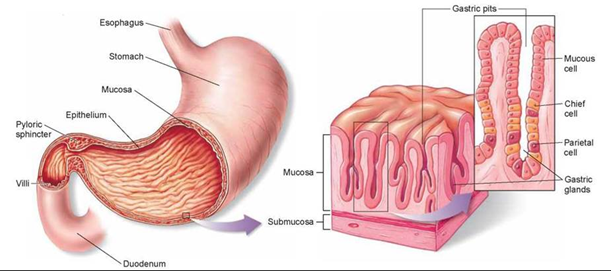
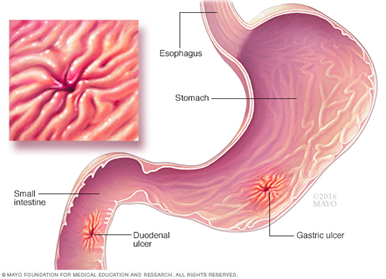
ulcer: too little mucus or too much acid
vomiting: reflex, abdominal muscles force stomach contents out. -> anti-peristaltic movement of the esophagus

- absorption of alcohol, caffeine, some medicines, water
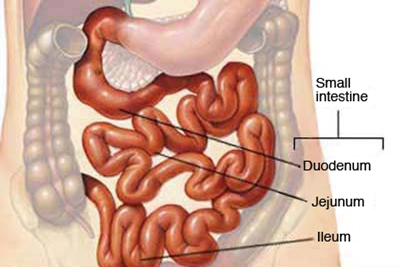
II. MIDGUT = SMALL INTESTINE
Digestion is finished, nutrients are absorbed
- duodenum 25-30 cm
- jejunum
- ileum
- Digestive glands:
- Liver
- stores glycogen, iron
- transforms nutrients
- produces proteins of blood plasma
- breaking down processes (e.g. haemoglobin)
- detoxifies
- produces bile:
- stored in gall bladder
- 1 litre / day
- bile acids, bile pigments, water, ions
- detergent -> emulsifies lipids (-> breaks lipids into small droplets that can be attacked by enzymes )
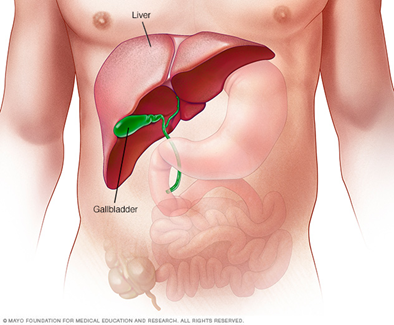
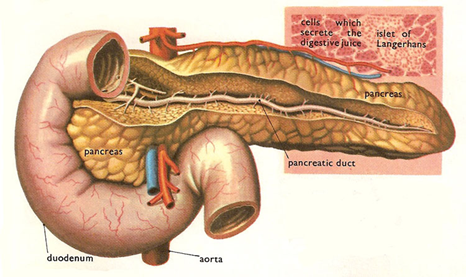
- Pancreas
- exocrine glands ->
- pancreatic juice: sodium bicarbonate – neutralizes the hydrochloric acid
- trypsin, chymotrypsin:
- proteins, polypeptides -> dipeptides
- Pancreatic amylase:
- polysaccharides -> disaccharides
- Glycogen and starch -> maltose
- Lipase:
- oils and fats -> monoglycerides / glycerol + fatty acids
- Nuclease:
- Nucleic acids -> nucleotides
- endocrine glands
- islets of Langerhans: 1-2%
- -> hormones: insulin, glucagon
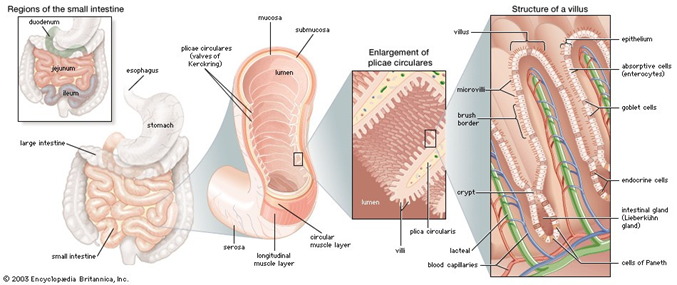
- Glands in the lining of the small intestine
- -> intestinal juice
- 1-3 litres
- Finishes digestion
- enzymes:
- Erepsin:
- Dipeptides -> amino acids
- Maltase, fructase, lactase:
- Disaccharides -> monosaccharides
- lactose intolerance cramps, bloated feeling, diarrhea
- Lipase:
- lipids -> monoglycerides + fatty acids
- Nuclease:
- Nucleic acids -> nucleotides
- Erepsin:
|
Digestive juice |
pH |
Digested nutrients |
||
|
Carbohydrates |
Proteins |
Fats |
||
|
Saliva |
7 |
Salivary amylase |
- |
- |
|
Gastric juice |
2 |
- |
Pepsin |
- |
|
Bile |
8 |
- |
- |
Emulsifies!! |
|
Pancreatic juice |
8 |
Pancreatic amylase |
Trypsin |
Lipase |
|
Intestinal juice |
7.5 |
(maltase, fructase, lactase) |
Erepsin |
Lipase |
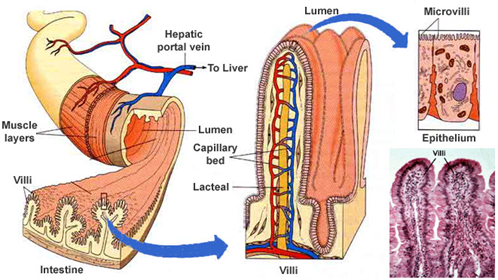
Absorption of nutrients
- villi
- fingerlike projections of the lining
- blood and lymph vessels inside it
- microvilli cover the surface of each villus
- extensions of plasma membrane
- increase the internal surface area to take up food molecules
- polar molecules -> into the blood
- apolar molecules -> into the lymph
III. HINDGUT
- 1-1.5m
- Caecum + vermiform appendix
- Colon:
- ascending colon,
- transversecolon,
- descending colon,
- sigmoid colon
- Rectum -> anus
- Millions of bacteria – symbiosis:
- vitamins B, K
- Protect against infections
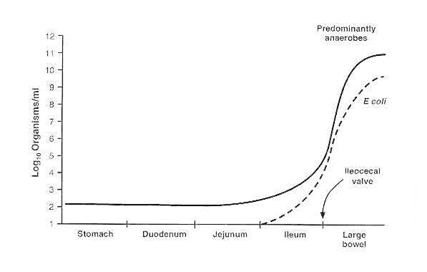
- No villi
- No digestion
- Absorption of water and minerals
- Forming feces from indigestible wastes
- Egestion of feces: peristalsis, abdominal press
Organic foods are produced using environmentally sound methods that do not involve modern synthetic inputs such as pesticides and chemical fertilizers, do not contain genetically modified organisms, and are not processed using irradiation, industrial solvents, or chemical food additives.
Food additives, such as artificial sweeteners, colorants, preserving agents, and flavourings may cause health problems such as increasing the risk of cancer
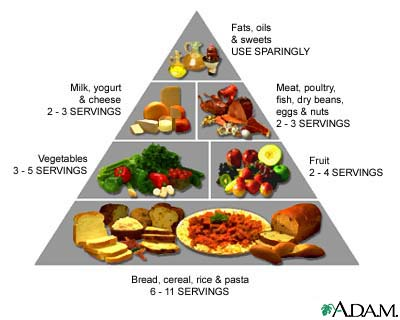
Healthy diet:
- Less fat (unsaturated), sugar and salt
- More fruits and vegetables
- Essential amino acids
- Vitamins, minerals
- Lots of water
Food pyramid
Body mass index (BMI)
a measure of body fat based on height and weight that applies to adult men and women. BMI calculator
BMI Categories:
Underweight = <18.5
Normal weight = 18.5–24.9
Overweight = 25–29.9
Obesity = BMI of 30 or greater
Diseases:
- ulcer (gastric, duodenal),
- caries - decay of a tooth
- icterus - a medical condition with yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes, arising from excess of the pigment bilirubin and typically caused by obstruction of the bile duct, by liver disease, or by excessive breakdown of red blood cells.
- cancer
- enteritis - inflammation of the intestine, especially the small intestine, usually accompanied by diarrhoea.
- hyperacidity
- haemorrhoid - a swollen vein or group of veins in the region of the anus.
An unhealthy diet is a major risk factor for a number of chronic diseases including: high blood pressure, diabetes, overweight/obesity, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer.
12 interesting facts about your digestive system
Name the parts of teeth the statements refer to.
Do this matching task about teeth.
Label the parts of a tooth.
Identify the parts of the human digestive system. Learningapps
The route of a nutrient. Gap filling task Leaningapps
Put the cards into the correct order, as food goes down the alimentary canal. Here
Group the organs of the alimentary canal here.
Find the parts of the human digestive system the statements refer to. here
The alimentary canal in numbers. Matching task.
A bejegyzés trackback címe:
Kommentek:
A hozzászólások a vonatkozó jogszabályok értelmében felhasználói tartalomnak minősülnek, értük a szolgáltatás technikai üzemeltetője semmilyen felelősséget nem vállal, azokat nem ellenőrzi. Kifogás esetén forduljon a blog szerkesztőjéhez. Részletek a Felhasználási feltételekben és az adatvédelmi tájékoztatóban.