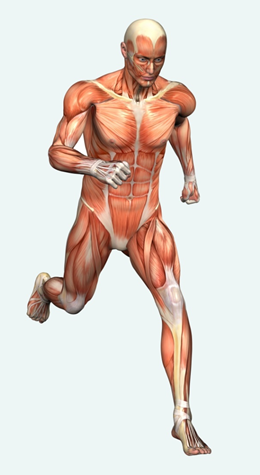
 Skeletal muscles:
Skeletal muscles:
- make up nearly half the body weight of an adult
- contraction: need E + O2 -> rich blood supply
- functions: active movement, heat generation, stores glycogen
Structure:
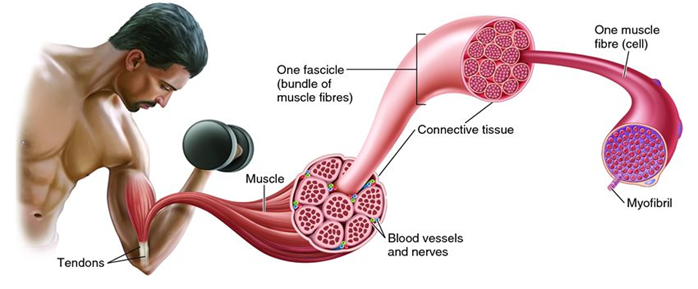
- cells = muscle fibres:
- long, have many nuclei
- contain myofibrils – contractile elements
- actin – thin
- myosin – thick
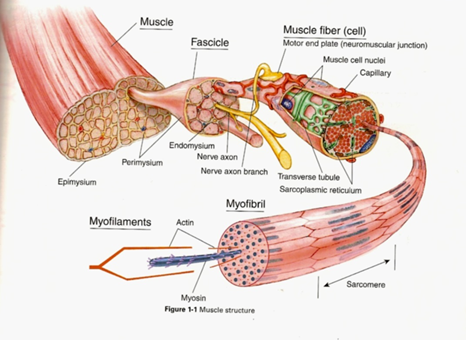
- gives a striped appearance à striated muscle
- we can move them at will à voluntary muscle
- muscle fibres form bundles of fibres
- surrounded by connective tissue
- blood supply, oxygen -> biological oxidation
- lack of oxygen -> fermentation (lactic acid) – pain in muscles (muscle soreness)
- nerves: trigger stimuli for contraction
Shape:
- spindle: on limbs
- flat: on the trunk
- circular: around openings (eyes, mouth, anus) -> closing
Operation:
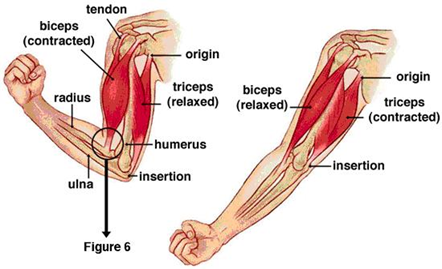
- to operate skeletal muscle needs to have both ends connected to the skeleton – tendons
- origin: end of muscle that remains fixed (closer to the trunk)
- insertion: end of muscle that moves the bone (farther from the trunk)
- antagonistic pairs of muscles act in opposition to each other
- one contracts - the other relaxes
- flexor: flexes limbs (biceps)
- extensor: extends a limb (triceps)
- g. when biceps muscle of the upper arm contracts, the opposing triceps muscle relaxes -> the elbow is bent
- one contracts - the other relaxes
- central nervous system -> signals -> contraction
-
muscle tone
is the continuous and passive partial contraction of the muscles
helps maintain posture, and it declines during sleep.
Unconscious nerve impulses maintain the muscles in a partially contracted state.
If a sudden pull or stretch occurs, the body responds by automatically increasing the muscle's tension.
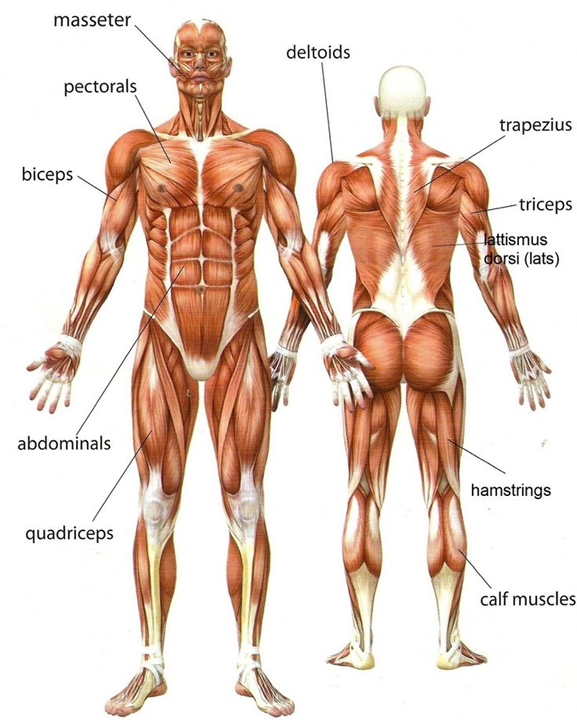
Examples for muscles:
- mimics muscles:
- origin and insertion on the skin – on the head
- sterocleidomastoid muscle (SCM)
- on the neck -> moves the head
- diaphragm
- at the bottom of the rib cage,
- separates the abdominal and thoracic cavities
- -> breathing
- intercostal muscles
- between the ribs -> breathing
- pelvic floor muscles (perineum)
- supports organs,
- helps continence
- chest muscles
- lift the arms and move them forward,
- help breathing
- abdominal muscles
- protect internal organs,
- stabilise, twist and bend the trunk
- maintain internal abdominal pressure.
- Abdominal press - exhalation, elimination of wastes, birth
Importance of regular exercise
- stronger muscular system,
- more stable skeletal system,
- better circulation,
- respiration,
- has a positive effect on our nervous system,
- reduces stress,
- helps weight loss

Types of training
- Fitness
- Skill
- Endurance / strength
Warm-up: important before training, stimulates circulation of muscles, prevents injuries


Muscle soreness -> treat with exercise -> blood can take away lactic acid to the liver
14 fun facts about your muscular system.
Learningapps labeling task
A bejegyzés trackback címe:
Kommentek:
A hozzászólások a vonatkozó jogszabályok értelmében felhasználói tartalomnak minősülnek, értük a szolgáltatás technikai üzemeltetője semmilyen felelősséget nem vállal, azokat nem ellenőrzi. Kifogás esetén forduljon a blog szerkesztőjéhez. Részletek a Felhasználási feltételekben és az adatvédelmi tájékoztatóban.