I. Types of bones
a) long bones

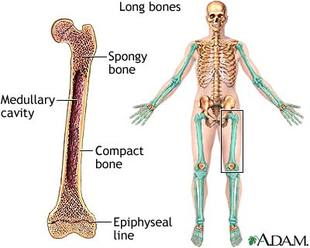
E.g.: femur, tibia, fibula, humerus, radius, ulna
b) flat bones
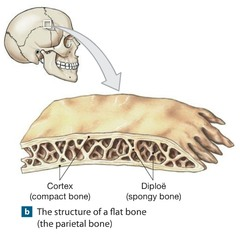
E.g.: scapula bones of the skull
II. Structure of bones
- cartilage
- at the end of long bones
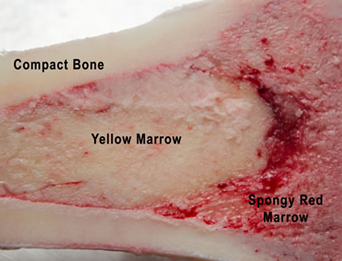
- compact bone:
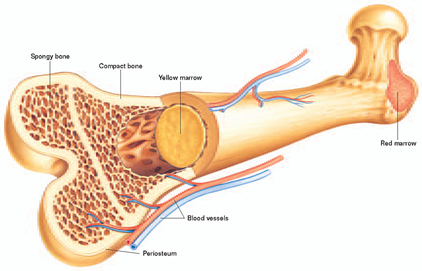
- concentric rings (lamellae)
- with central canals
- spongy bone

- numerous cavities
- trabeculae – can be rearranged
- red bone marrow
- medullary cavity
- yellow bone marrow
- periosteum
- covers the surface
- rich in blood vessels and nerves
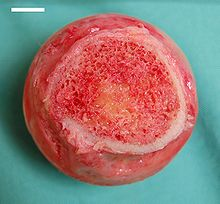
Bone marrow:
- red bone marrow:
Produces blood cells
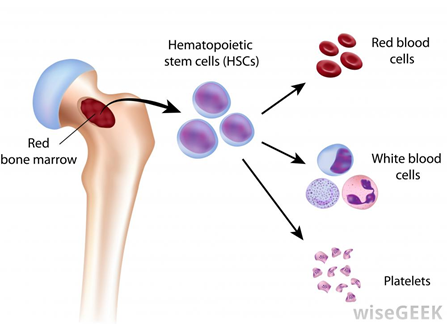
- yellow bone marrow:
- mostly adipose tissue
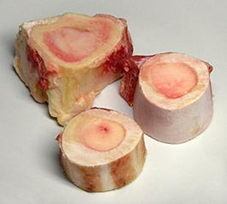
Can convert into each other.
III. Bone connections:
Joints / articulations – where bones meet
a) fixed
sutures:
between cranial bones
fontanels: allow slight movement during birth
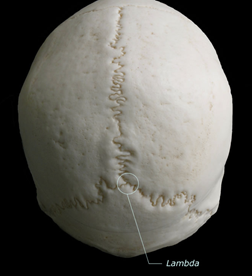
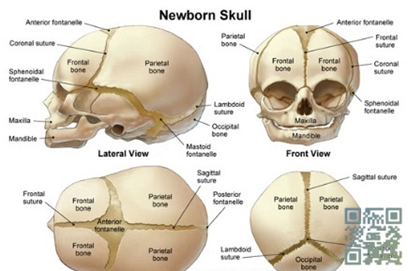
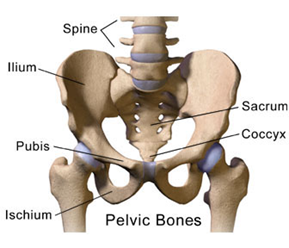
fusion :
sacrum, pelvis
cartilaginous joint:
cartilaginous discs between vertebrae
between ribs and sternum
slightly movable
b) movable
synovial joints:
joints of the ankle, elbow, shoulder, knee
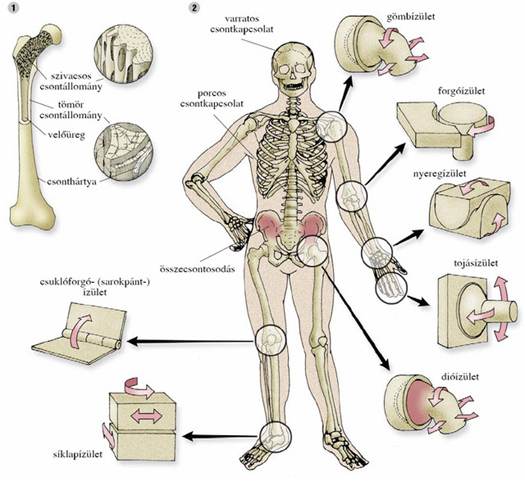
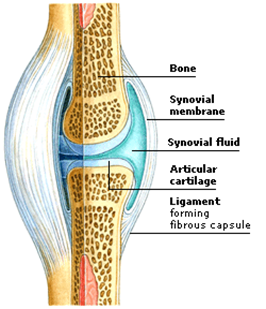
IV. Disorders:
- dislocation: (=ficam) bones are separated, displaced at a joint
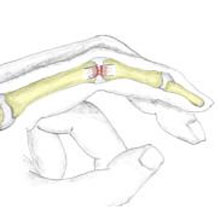
- sprain: (=rándulás) stretching or tearing ligaments
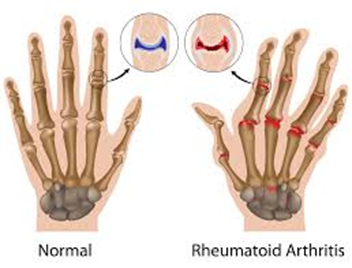
- arthritis: joint inflammation, autoimmune reaction
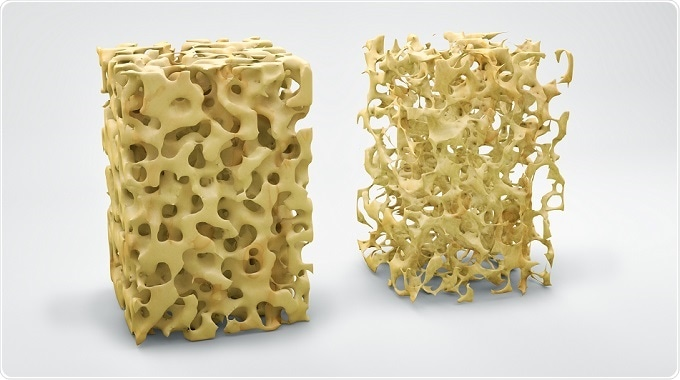
- Osteoporosis:
extreme bone loss -> easily broken
peak density at 35
smoking, heavy drinking, lack of exercise
prevention: plenty of Ca2+, regular exercise
A bejegyzés trackback címe:
Kommentek:
A hozzászólások a vonatkozó jogszabályok értelmében felhasználói tartalomnak minősülnek, értük a szolgáltatás technikai üzemeltetője semmilyen felelősséget nem vállal, azokat nem ellenőrzi. Kifogás esetén forduljon a blog szerkesztőjéhez. Részletek a Felhasználási feltételekben és az adatvédelmi tájékoztatóban.