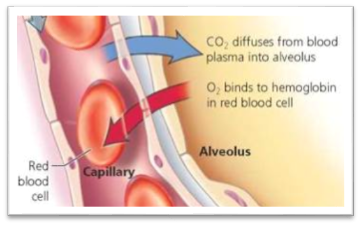
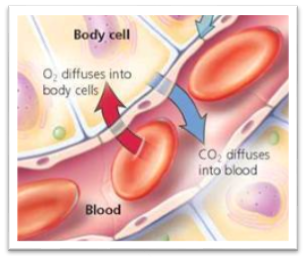
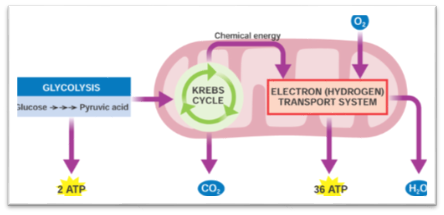
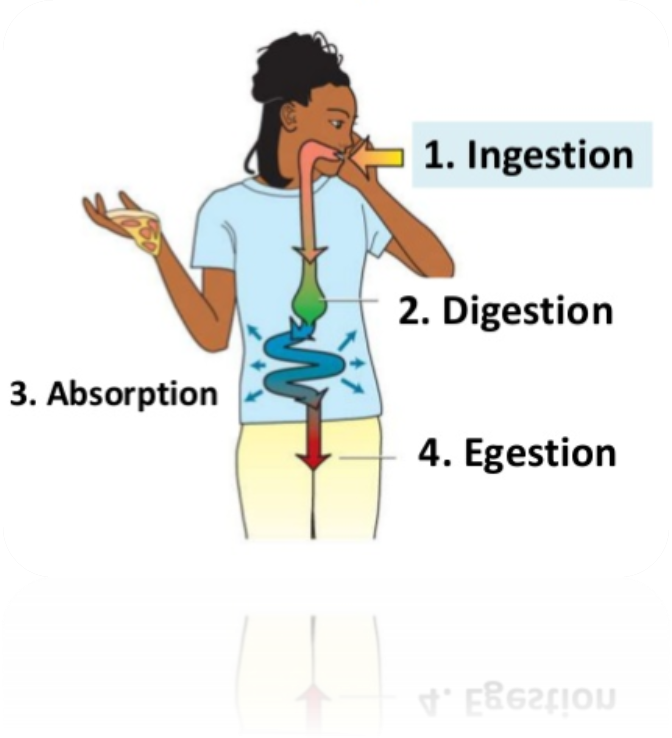
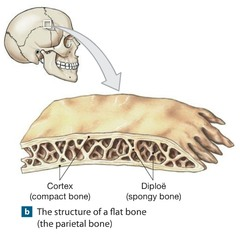
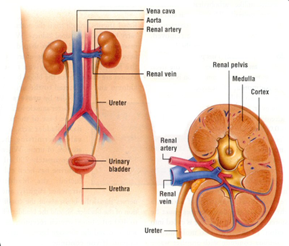
The Human Excretory System maintains homeostasis by regulating body fluid volume, ion concentration, pH, and elimination of metabolic wastes. 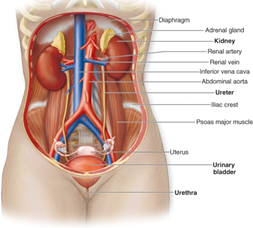
- Parts:
- a pair of kidneys
- a pair of ureters
- a urinary bladder
- a urethra
- The kidney:
- dark purplish – immense blood supply
- shaped like a bean
- located at both sides of the vertebral column
- in the back of the abdominal cavity
- easily detached
- held in position by connective tissue and protected by a ...