Human Locomotion System
Main parts of the human locomotion system:
- skeletal system (bony endoskeleton) -> passive
- muscular system (skeletal muscles) -> active

Functions of vertebrate skeleton:
- supports – framework for the body
- movement – skeletal muscles attach to it
- protects internal organs(brain, heart, lungs)
- stores minerals: calcium, phosphate
- produces blood cells
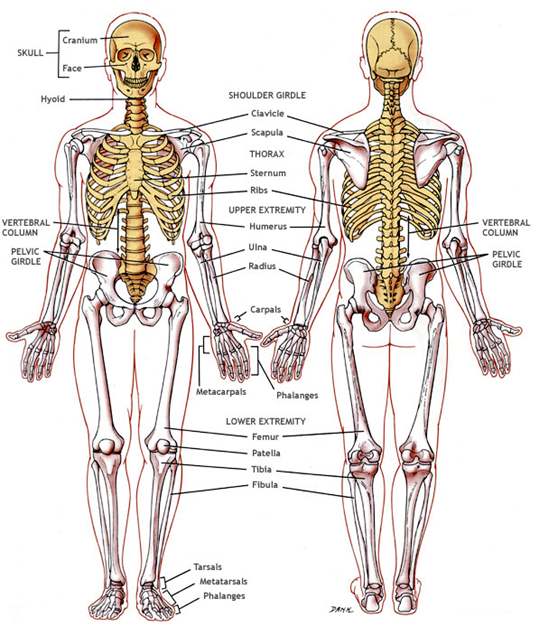
The skeletal system
206 bones (270 at birth – fusing together)
- Skull
- Trunk
- Limbs
a) Skull
- cranial bones (cranium):
- sphenoid bone,
- frontal bone,
- parietal bone,
- occipital bone,
- temporal bone
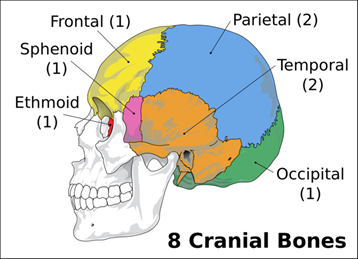
- connected by sutures
- hole in the occipital bone = foramen magnum
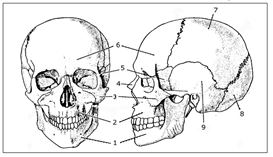 - facial bones
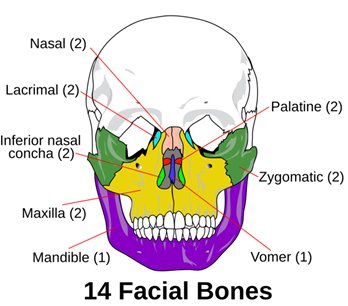
- facial bones
- mandible
16 teeth
connected to the cranium with movable joints
chin protuberance -> speech - maxilla
16 teeth - zygomatic bone
- nasal bone
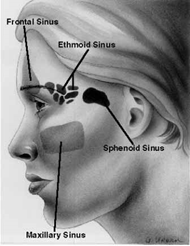
sinuses (=cavities)
-> reduce the weight of the skull
-> resonance -> voice
e.g. Maxillary sinus – in the maxilla
b) Trunk
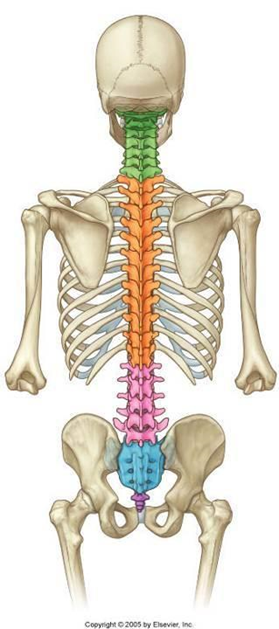
- vertebral column
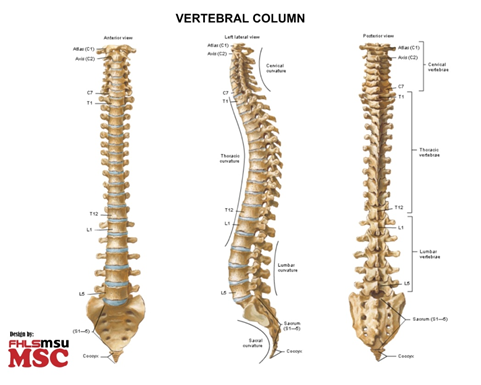
- 33 vertebrae
- Body, hole, arch, projections: 2 lateral/transverse processes, spinous process
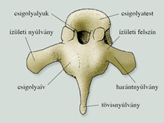
- protects the spinal cord
- supports the head
- 4 curves -> double S – shape
- -> Flexible, absorbs shocks when walking or running

- regions:
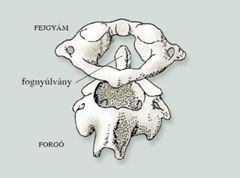
- cervical 7
- thoracic 12
- lumbar 5
- sacral 5 -> sacrum
- coccygeal 3-5 -> coccyx

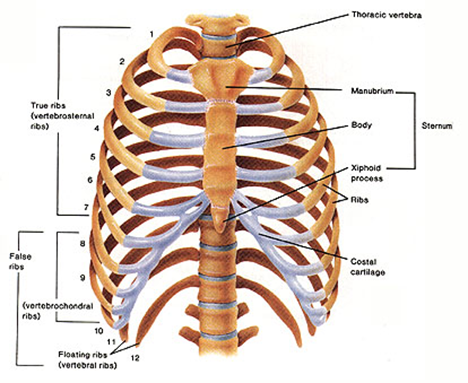
-12 pairs of ribs + sternum -> rib cage:
- protects the heart and lungs; breathing
- 7 pairs of true ribs (directly attached to the sternum through the costal cartilage)
- 3 pairs of false ribs (share a common cartilaginous connection to the sternum)
- 2 pairs of floating ribs (attached to the vertebrae only)
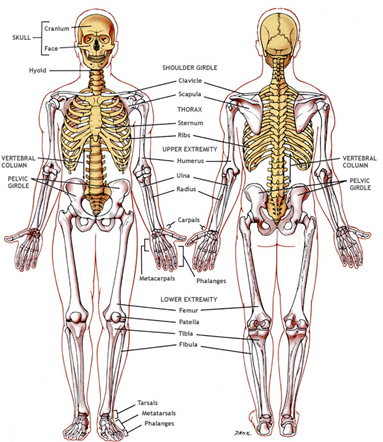
c) Limbs
- upper extremities
- lower extremities
- Pectoral / shoulder girdle
- Pelvic / hip girdle
- anchor limb bones to the trunk
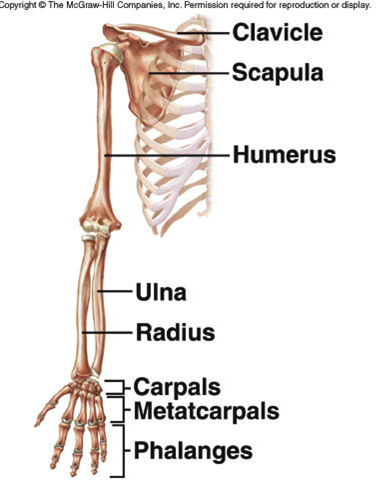 upper extremities
upper extremities
- humerus (upper arm bone)
- radius
- ulna
- carpals
- metacarpals
- phalanges
pectoral / shoulder girdle
- 2 clavicles (collar bones)
- 2 scapulas (shoulder blades)
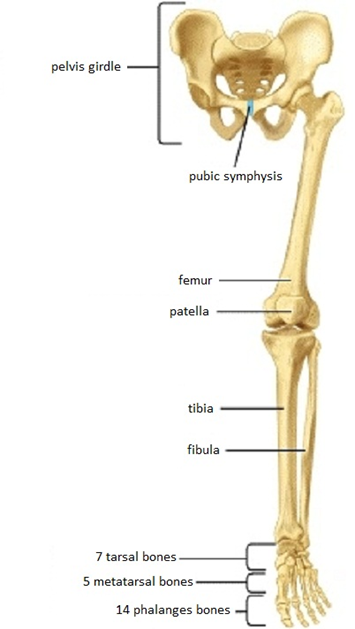 lower extremities
lower extremities
- femur (thighbone)
- patella
- tibia
- fibula
- tarsals
- metatarsals
- phalanges
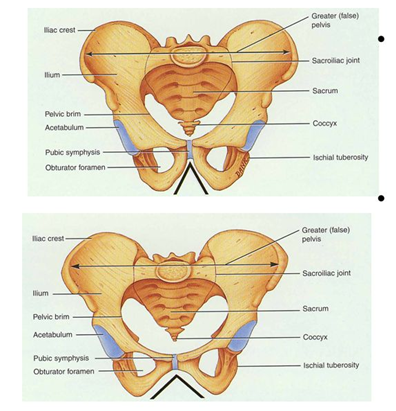
pelvic / hip girdle
- 2 hip bones: (ilium, ischium, pubis)
- sacrum
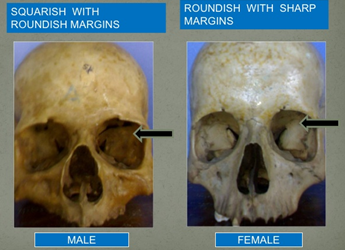
Skeletal differences in men and women:
- female bones are usually lighter and thinner than more robust male bones
- the female pelvis is shallower and wider than the male's -> makes childbirth easier
- female cranium has sharper superior margins of the orbits
Health problems
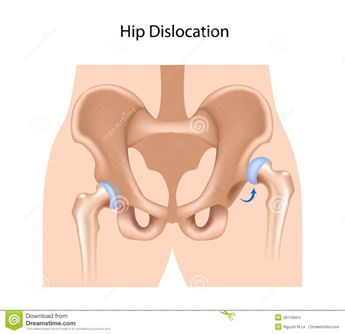
- Dislocation of hip:
- more common in girls;
- must be detected early
- when it can be easily treated by a few weeks of traction,
- exercise when changing nappy

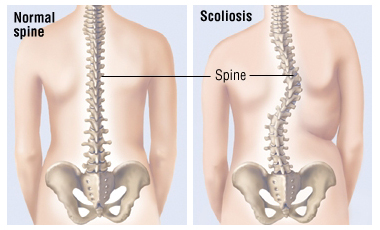
- Scoliosis
- deformity of the backbone.
- Prevention, bed, chair, regular exercise, swimming.
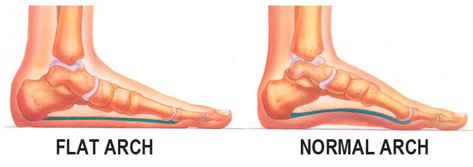
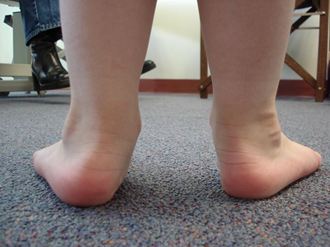
- Flat feet
- the arch of the foot collapses,
- the entire sole is in contact with the ground
- -> foot gymnastics and going barefoot,
- shoe inserts

Use Quizlet flashcards to learn the names of bones.
21 amazing facts about the human skeleton
Identify the bones of the skull in this Learningapps task.
Label the bones of the upper limb in this Learningapps task.
Label the bones of the lower limb in this Learningapps task.
Label the bones of the skeleton in this Learningapps task.
Identify the bones of the skeleton in this Learningapps task.
A bejegyzés trackback címe:
Kommentek:
A hozzászólások a vonatkozó jogszabályok értelmében felhasználói tartalomnak minősülnek, értük a szolgáltatás technikai üzemeltetője semmilyen felelősséget nem vállal, azokat nem ellenőrzi. Kifogás esetén forduljon a blog szerkesztőjéhez. Részletek a Felhasználási feltételekben és az adatvédelmi tájékoztatóban.