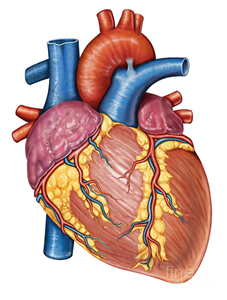
In the thoracic cavity, lies between the lungs, behind the breast bone
Structure
- fist-sized
- layers:
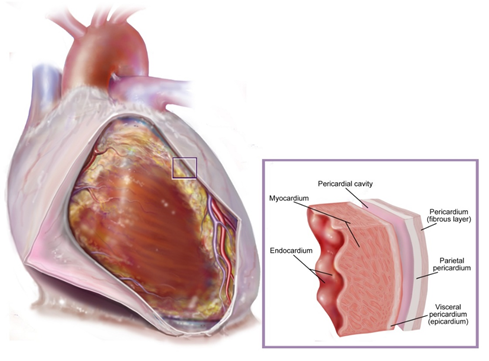
- pericardium – tough protective sac
- heart muscle - myocardium
- endocardium -> valves
- cardiac muscle:
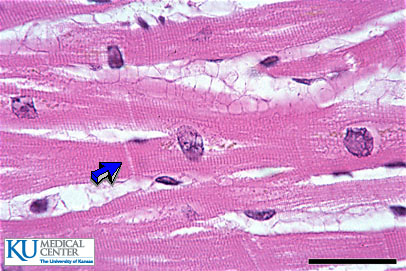
never gets tired (doesn’t fatigue)
striated muscle
involuntary
cells branch
thickest in left ventricle’s wall
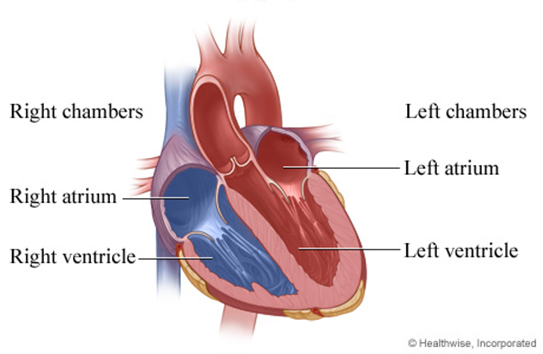
- four-chambered: 2 atria + 2 ventricles
- heart valves:
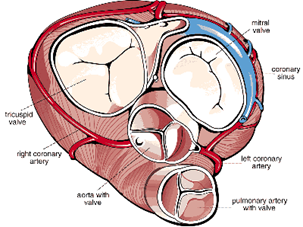
- ensure a one-way flow of blood /prevent the backflow of blood
- flaps of connective tissue
- open and close passively because of pressure differences
- like a door, which only opens in one direction.
- atrioventricular (AV) valves separate atria from ventricles
- stabilized by cord-like tendons
- papillary muscles (contract in synchrony with the ventricles -> tension)
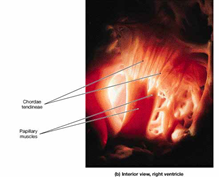
- => valves cannot turn inside out
- semilunar valves separate ventricles and arteries
- consist of three crescent-shaped cusps
- consist of three crescent-shaped cusps
- atrioventricular (AV) valves separate atria from ventricles
Learningapps practice
Heart cycle
2 steps:
- atrial contraction – ventricular relaxation (diastole)
- atrial relaxation – ventricular contraction (systole)
The atria contract together and then the ventricles contract together.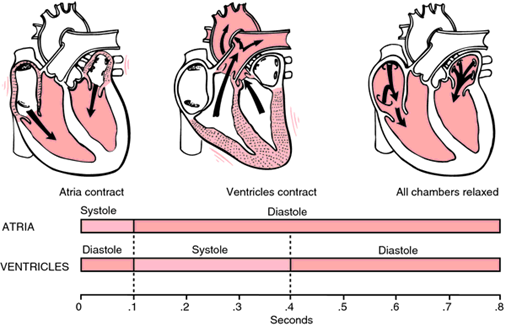
Your heart beats 100,000 times in one day and about 35 million times in a year.
Watch this video.
Blood pressure
- can be measured with a blood pressure meter
- systolic pressure over diastolic pressure
- measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg),
- above the surrounding atmospheric pressure
Heartbeat - heart sounds
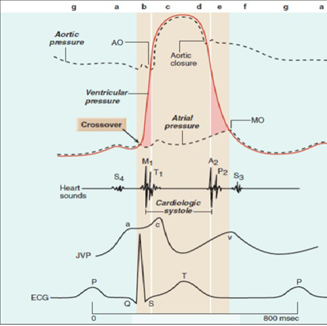
- Lub-dub sound
- caused by the closing of heart valves.
- 1st the closing of the AV valves.
- 2nd the closing of the semilunar valves.
- using a phonocardiograph:
- 3rd sound - filling with blood when ventricles relax
- 4th sound - atrial contraction
How much blood does your heart pump per minute?
- 70ml/contraction
- 72 contractions/min
- At rest pumps 5 litres of blood /minute
- Strenuous exercise -> 7 times that amount
- Unfit person – frequency increases
- Fit people – blood volume increases
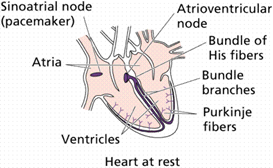
Conduction system
- Own automatic pacemaker:
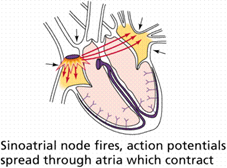
- sinoatrial (SA) node in right atrium sends out a stimulus -> atria contract
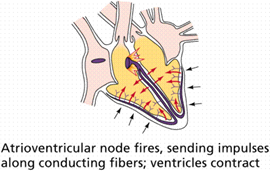
- atrioventricular (AV) node sends impulses along conducting fibers -> ventricles contract
-
sinoatrial (SA) node fires 70/min,
atrioventricular (AV) node fires 40/min
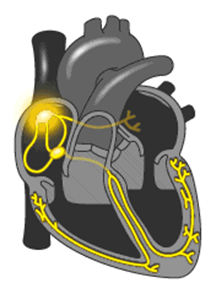
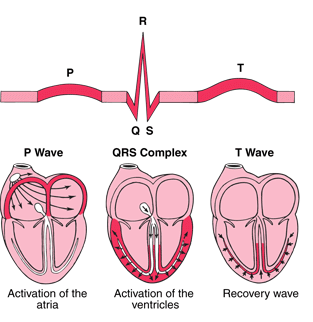
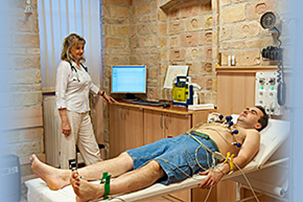
ECG electrocardiogram
recording the electrical activity of the heart
with electrodes placed on the skin
The blood circuits of the cardiovascular system:
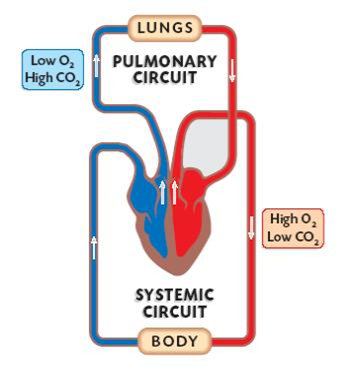
Pulmonary circuit
right ventricle -> pulmonary arteries (deoxygenated blood) -> capillaries of lungs -> pulmonary veins (oxygenated blood) -> left atrium.
Systemic circuit
left ventricle -> aorta -> systemic arteries of the body -> body capillaries -> veins -> right atrium of the heart.
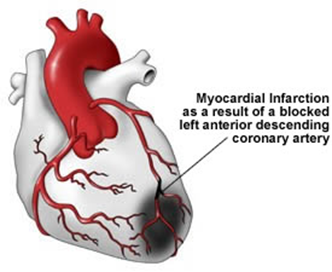
Coronary circulation
- supplies the heart with blood
- heart attack:
- lack of oxygen -> cells die
- cause: arteriosclerosis
A bejegyzés trackback címe:
Kommentek:
A hozzászólások a vonatkozó jogszabályok értelmében felhasználói tartalomnak minősülnek, értük a szolgáltatás technikai üzemeltetője semmilyen felelősséget nem vállal, azokat nem ellenőrzi. Kifogás esetén forduljon a blog szerkesztőjéhez. Részletek a Felhasználási feltételekben és az adatvédelmi tájékoztatóban.