The Human Excretory System maintains homeostasis by regulating body fluid volume, ion concentration, pH, and elimination of metabolic wastes.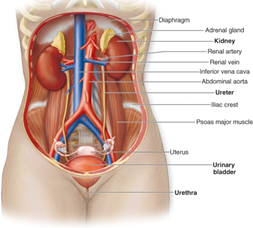
- Parts:
- a pair of kidneys
- a pair of ureters
- a urinary bladder
- a urethra
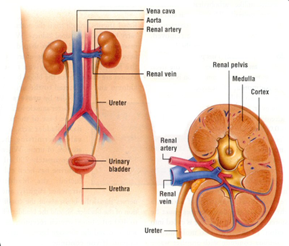
- The kidney:
- dark purplish – immense blood supply
- shaped like a bean
- located at both sides of the vertebral column
- in the back of the abdominal cavity
- easily detached
- held in position by connective tissue and protected by a layer of fat
- capsule: fibrous connective tissue
- renal hilum: the renal artery enters and the renal vein and ureter leave
- cortex
- medulla: made up of renal pyramids
- pelvis: central cavity, leads into the ureter
- The nephron:
- functional unit of kidney
- 1-2 million / kidney
- Functions: filters, reabsorbs, excretes
- Parts:
- Renal corpuscle – in the cortex
- capillary knot = glomerulus (branched capillaries)
- Bowman’s capsule (double-walled, cup-shaped structure around the glomerulus)
- Renal tubule
- proximal convoluted tubule
- loop of Henle
- descending limb
- hairpin turn
- ascending limb
- distal convoluted tubule
- Renal corpuscle – in the cortex
- Production of urine
- glomerulus
Blood plasma is filtered through the glomerulus into the Bowman’s capsule
=> (ultra)FILTRATE = protein-free blood plasma
- water, glucose, amino acids, salts, urea
- 180 litres / day
- Why? Arteriole entering the glomerulus has greater diameter than the arteriole leaving the glomerulus -> high blood pressure -> pushes blood plasma through the wall of the capillary
- Passive movement – depends only on pressure
(8kPa in capillary knot, 3kPa in capsule)
- No reabsorption
- proximal convoluted tubule
- filtrate 180 l -> urine 5 l / day
- reabsorption: -> tubule cells -> capillaries
- almost 100% glucose
- 80% Na+, K+ actively
- Vitamins
- amino acids
- 75% water – passively by osmosis

- loop of Henle
- descending limb: the filtrate becomes more concentrated, because water passes
- hairpin turn: filtrate is the most concentrated here
- ascending limb: wall of tubule is impermeable to water -> sodium reabsorption is not followed by water diffusion -> filtrate becomes less concentrated
- d) distal convoluted tubule
- permeable to water -> water leaves, volume is reduced
- reabsorption of water and ions depend on water and ion concentration of blood
- place where hormones take effect
- collecting ducts
- water reabsorption
- URINE:
- no sugar (<- diabetes mellitus)
- no proteins
- urea
- ions
-> pelvis -> ureter(smooth muscle - peristalsis) -> urinary bladder: stores – pressure on wall, sphincter (smooth + voluntary muscle) -> urethra
Secretion:
- by tubule cells into the tubule (descending limb, distal t.)
- secreted substances diffuse from blood capillaries into tubule cells
- H+, K+, aspirin, penicillin, drugs -> drug testing for athletes (muscle-building steroids)
- Hormonal regulation
- ADH (or vasopressin) antidiuretic hormone – from pituitary gland -> stimulates water reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubules, by making the tubule more permeable to water. Alcohol inhibits ADH -> more urine
- aldosterone: from adrenal cortex promotes Na+ reabsorption in distal tubules
- diseases
Kidney failure:
Artificial kidney – dialysis - only filtration
Kidney transplant
Nephritis: inflammation of the kidney due to bacterial contamination
Cystitis: urinary bladder inflammation – frequent, painful urination, pus in urine
Urinary incontinence - involuntary leakage of urine
Kidney stones:
- due to contamination, abnormal metabolism, too concentrated urine
- made up of Ca-phosphate, Ca-oxalate, urea
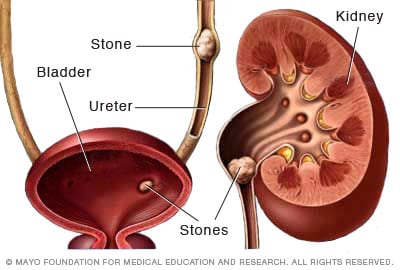
- stone develops in collecting ducts -> gets into the pelvis and grows -> enters the ureter – sudden, painful cramp
- treatment:
- surgical
- get the patient pass the stone ( high fluid intake, ultrasound)
|
|
Bowman’s capsule and glomerulus |
proximal convoluted tubule
|
loop of Henle
|
distal convoluted tubule |
|
Location |
cortex |
cortex |
cortex & medulla |
cortex
|
|
What happens? |
Filtration
|
Reabsorption: Glu, Na+, K+, H2O, vitamins, amino acids |
Excretion & reabsorption of Na+
most concentrated |
Reabsorption & excretion
less concentrated |
|
Hormonal control |
__
|
__ |
__ |
+ ADH |
|
Name of product |
filtrate
|
__ |
__ |
urine |
|
Amount |
180 l
|
18 l |
__ |
1-1.5 l |
A bejegyzés trackback címe:
Kommentek:
A hozzászólások a vonatkozó jogszabályok értelmében felhasználói tartalomnak minősülnek, értük a szolgáltatás technikai üzemeltetője semmilyen felelősséget nem vállal, azokat nem ellenőrzi. Kifogás esetén forduljon a blog szerkesztőjéhez. Részletek a Felhasználási feltételekben és az adatvédelmi tájékoztatóban.