About 5 litres
pH 7.4
Function:
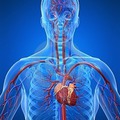
- Transports
- respiratory gases
- nutrients
- waste materials
- hormones
- enzymes
- regulates
- body temperature
- pH
- protects against
- blood loss
- foreign agents
Blood components: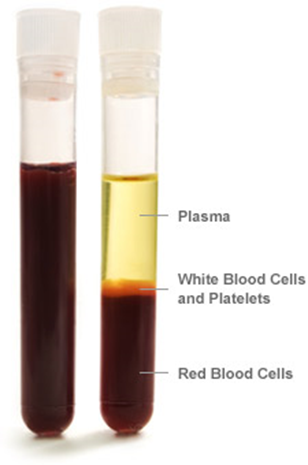
|
Blood plasma 55% |
Cellular elements 45% |
||||
|
Water
|
Ions |
Small organic molecules |
Proteins 8% |
Other
|
- red blood cells - white blood cells - platelets |
|
90%
|
Na+ K+ Ca2+ Cl- HCO3-
|
Nutrients: glucose amino acids fatty acids cholesterol vitamins Wastes: bilirubin urea |
a) albumins - simple proteins - provide osmotic pressure - transport (lipids, amino acids, ions) - buffer effect b) globulins - complex proteins - transport (hormones, lipids, vitamins) - in immune responses (immune globulins, antibodies) c) fibrinogen - in blood clotting |
Respiratory gases, hormones, enzymes |
|
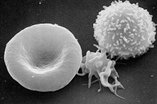
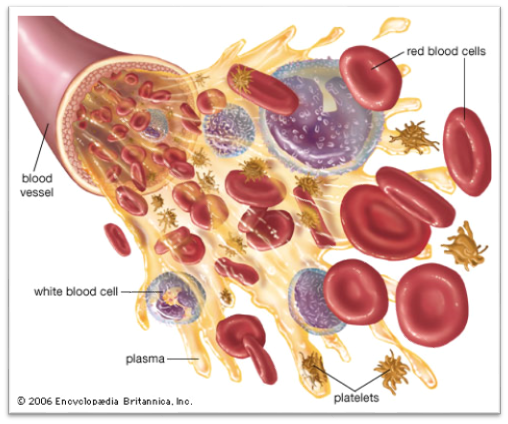
Cellular elements:
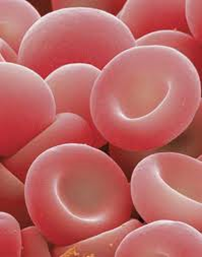
- Red blood cells / erythrocytes
- biconcave shape, disk (doughnut shape)
- 5-5.5 million / mm3
- sports and altitude increase the number
- 7μm
- lose nucleus during maturation -> can’t reproduce
- can’t move – only passively
- produced in red bone marrow (vitamin B12)
- destroyed in liver, spleen (after 120 days)
Functions:
- transports oxygen -> haemoglobin in its cytoplasm
- in lungs picks up oxygen -> oxyhemoglobin
- in tissues O2 pressure is low -> releases oxygen
- transports CO2
Disease:
- anaemia: low number of red blood cells / haemoglobin concentration; lack of vitamin B12 , Fe, folic acid
- sickle-cell anaemia: inherited disease, abnormal haemoglobin, sickle shaped cells are stiff -> block blood flow, can cause pain, serious infections, and organ damage, leads to death.
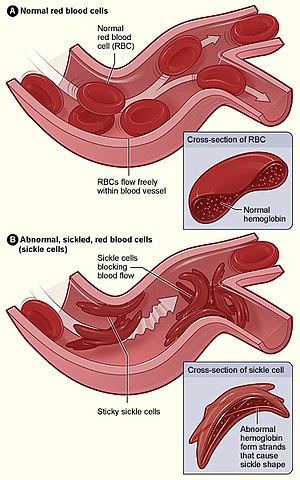

- haemolysis: breakdown of red blood cells before time (poison of bees, snakes -> membrane damaged)
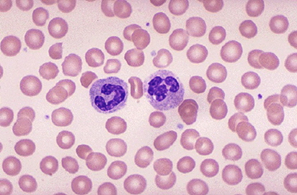
2. White blood cells / Leukocytes
- variable shape
- amoeboid movement -> can leave capillaries -> site of infection
- 6-8000 / mm3
- 5-20μm
- have a nucleus
- produced in red bone marrow
- destroyed in liver (after 1- 2 weeks)
Function:
- immune response – combat microbes and their toxins
Types: 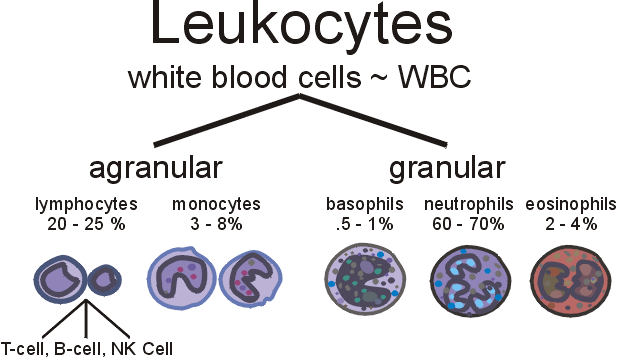
- granulocytes: leave to the site of infection – endocytosis -> die
- monocytes: (largest) leave to the site of infection – endocytosis -> die
- lymphocytes: mature in lymphatic tissue, recognize
Disease:
- leukaemia: many immature white blood cells <- abnormal bone marrow
- chemotherapy, irradiation to kill tumour cells, bone marrow transplantation
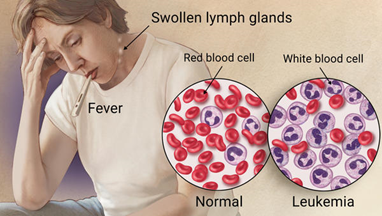
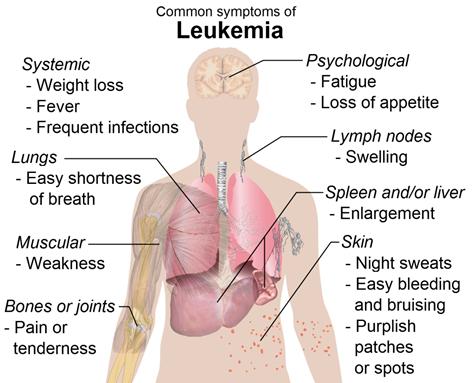
3. Platelets / Thrombocytes
- 2-4μm
- 150-300 thousand / mm3
- fragments of the cytoplasm of large cells
- -> no nucleus
- produced in red bone marrow
- destroyed in liver, spleen (after 8-9 days)
Function:
- blood clotting:
- platelets coagulate ( stick to rough surfaces) -> release chemicals
- vessel constricts
- clot formation: 13 protein factors
activator complex
prothrombin -> thrombin (vitamin K, Ca2+)
fibrinogen -> fibrin -> insoluble network of threads
clot soon begins to shrink -> forms a scab

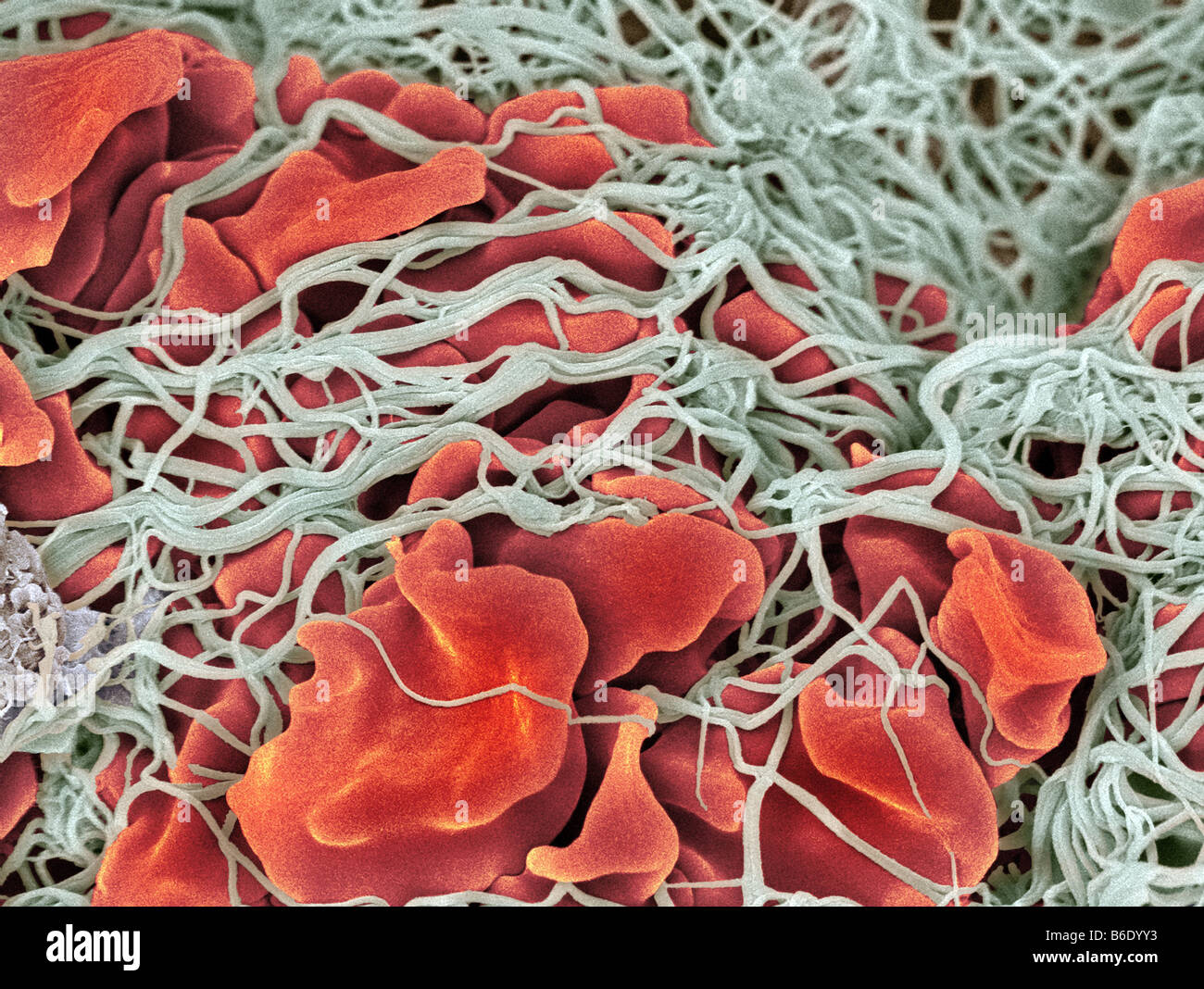
Disease:
- haemophilia: inability to stop bleeding (many types)
- arteriosclerosis: rough surface of vessels -> clot formation
- > thrombus can block an artery
- in heart -> heart attack
- in brain -> stroke
-> can break loose (-> embolus) -> block smaller arteries
- in lungs -> pulmonary embolus
- in brain -> fainting, limb weakness
Risk factors: aging, smoking, high blood pressure, fats in blood, diabetes.
Learningapps practice here
A bejegyzés trackback címe:
Kommentek:
A hozzászólások a vonatkozó jogszabályok értelmében felhasználói tartalomnak minősülnek, értük a szolgáltatás technikai üzemeltetője semmilyen felelősséget nem vállal, azokat nem ellenőrzi. Kifogás esetén forduljon a blog szerkesztőjéhez. Részletek a Felhasználási feltételekben és az adatvédelmi tájékoztatóban.